Recently, our project collaborated with Dr. Dongyi He in effects of (5R)-5-Hydroxytriptolide to epigenetic changes of LFS from RA was accepted by Scientfic Reports
Tripterygium is a traditional Chinese medicine that has widely been used in the treatment of rheumatic disease. (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8) is an extracted compound from Tripterygium, which has been shown to have lower cytotoxicity and relatively higher immunosuppressive activity when compared to Tripterygium. However, our understanding of LLDT-8-induced epigenomic impact and overall regulatory changes in key cell types remains limited. Doing so will provide critically important mechanistic information about how LLDT-8 wields its immunosuppressive activity. The purpose of this study was to assess the effects of LLDT-8 on transcriptome including mRNAs and long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) by a custom genome-wide microarray assay. Significant differential expressed genes were validated by QPCR. Our work shows that 394 genes (281 down- and 113 up-regulated) were significantly differentially expressed in FLS responding to the treatment of LLDT-8. KEGG pathway analysis showed 20 pathways were significantly enriched and the most significantly enriched pathways were relevant to Immune reaction, including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction (P = 4.61 × 10−13), chemokine signaling pathway (P = 1.01 × 10−5) and TNF signaling pathway (P = 2.79 × 10−4). Furthermore, we identified 618 highly negatively correlated lncRNA-mRNA pairs from the selected significantly differential lncRNA and mRNA including 27 cis-regulated and 591 trans-regulated lncRNA-mRNAs modules. KEGG and GO based function analysis to differential lncRNA also shown the enrichment of immune response. Finally, lncRNA-transcription factor (TF) and lncRNA-TF-mRNA co-expression network were constructed with high specific network characteristics, indicating LLDT-8 would influence the expression network within the whole FLS cells. The results indicated that the LLDT-8 would mainly influence the FLS cells systemically and specially in the process of immune related pathways.
…
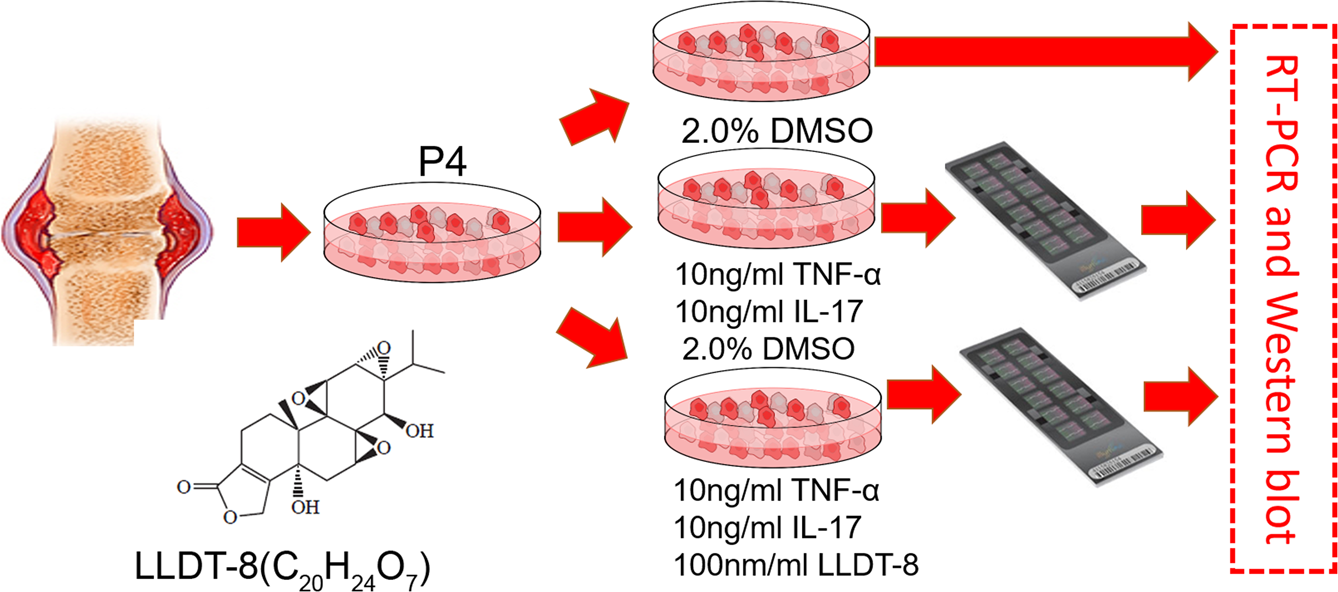
The aim of this study was designed to identify the mechanism of immuno-impressive function of LLDT-8 and identify potential ncRNA targets of LLDT-8. We applied TNF-α and IL-17 to induce an inflammatory status in the cells so that we can observe the LLDT-8 effect easily compared with treatment to normal FLS cell directly. We then assessed the effects of LLDT-8 on the regulation of gene expression on mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in FLS isolated from RA patients. Agilent Human lncRNA (4 × 180 K, Design ID: 062918) was applied in present study to provide genome-wide ncRNA and mRNA expression profile. With this study, we aimed to demonstrate how LLDT-8 treatment significantly impacts the process of immune regulation. …
Continue reading at (5R)-5-Hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8) induces substantial epigenetic mediated immune response network changes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients
…
NCBIBuild 35 ==> hg17; NCBIBuild 36 ==> hg18; NCBIBuild 37 ==> hg19; NCBIBuild 38 ==> hg38
- All the figures are only used for non-profit education. reminding me if infrigement happens
